Preparing Alcohol
Alcohols can be prepared by using 2 methods
- Hydration of alkene
- Fermentation
Hydration of Alkene
- When we discuss the chemical properties of alkenes, we have learned that, when alkenes undergo addition reaction with steam, alcohol will be produced. (see hydration of alkenes).
- Equations below shows the hydration of ethene and propene to produce ethanol and propanol respectively.
Hydration of Ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
Hydration of Propene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
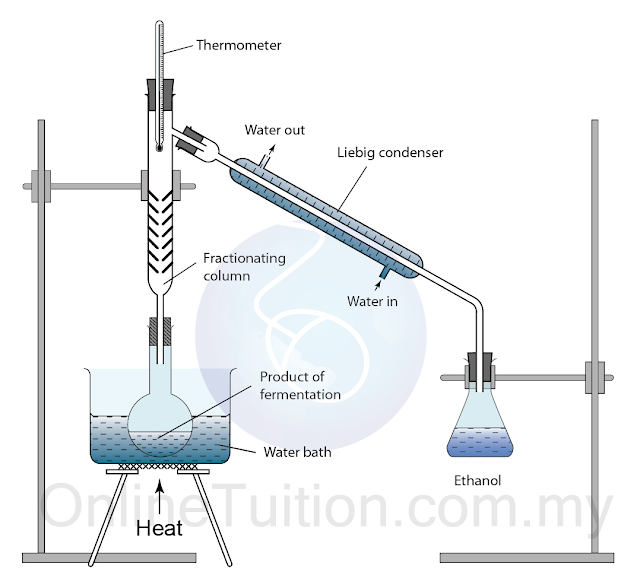
Fermentation
- This method only applies to ethanol.
- Fermentation is the chemical process which microorganism such as yeast act on carbohydrate to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.
- When yeast is added to sugar (example: glucose), fermentation occurs. During fermentation, the yeast produce an enzyme called zymase. The zymase enzyme breaks down the glucose molecules to simpler molecule, namely ethanol and carbon dioxide.
\[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\xrightarrow{{yeast}}2{C_2}{H_5}OH + 2C{O_2}\] - Yeast is killed by ethanol concentrations in excess of about 15%, and that limits the purity of the ethanol that can be produced.