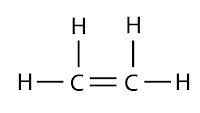Hydrocarbon
MUST Remember!
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen.
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen.
 |
| Saturated Hydrocarbon |
- Hydrocarbon is a compound made out of the elements carbon and hydrogen only.
- Examples of hydrocarbon are alkane, alkene and alkyne.
- Hydrocarbons can be divided into two groups:
- saturated hydrocarbon
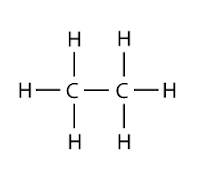
Saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons where all its carbon atoms are tied to each other through single covalent bond only. Examples: alkanes - unsaturated hydrocarbon
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons which contain at least one double covalent bond among its carbon atoms. Examples: alkenes
- Ethanol ( C2H5OH ), ethanoic acid (CH3COOH), metal methanoate (HCOOCH3), chloromethane (CH3Cl) and others are not hydrocarbons because the molecule contains other elements such as chlorine or oxygen other than carbon and hydrogen.
MUST Know!
- Saturated – All single bond between carbons
- Unsaturated – Has at least one double/triple bond between carbons
Comparing Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
| Saturated Hydrocarbon | Unsaturated Hydrocarbon | |
| Combustion | Produce less soot | Produce more soot |
| Reaction with bromine water | The brown colour of bromine remain unchanged | Decolourise the brown colour of bromine |
| Reaction with potassium manganate(VII) solution | The purple colour of potassium manganate (VII) solution remain unchanged | Decolourise the purple colour of potassium manganate (VII) solution |
Sources of Hydrocarbon:
The main sources of hydrocarbons are
- Coal
- Natural gas
- Petroleum
Combustion of Hydrocarbon
All hydrocarbons undergo combustion with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (or carbon monoxide/carbon) and water. There are 2 types of combustion:
Note:
- Complete combustion – organic compounds burn completely which form CO2 and H2O
- Incomplete combustion– organic compounds burn with limited supply of O2 which form C (soot), CO, CO2 and H2O.
Example
Complete combustion
C2H6 + 7/2 O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
C3H6 + 9/2 O2 → 3CO2 + 3H2O
Incomplete combustion
C2H6 + 5/2 O2 → 2CO + 3H2O
C2H6 + 3/2 O2 → 2C + 3H2O
C3H6 + 3O2 → 3CO + 3H2O
C3H6 + 3/2 O2 → 3C + 3H2O
Note:
- The soot from the combustion of a hydrocarbon depends on the percentage of carbon it contains.
- Higher carbon percentage in the hydrocarbon molecule will result sootier flame.