Experiment 2
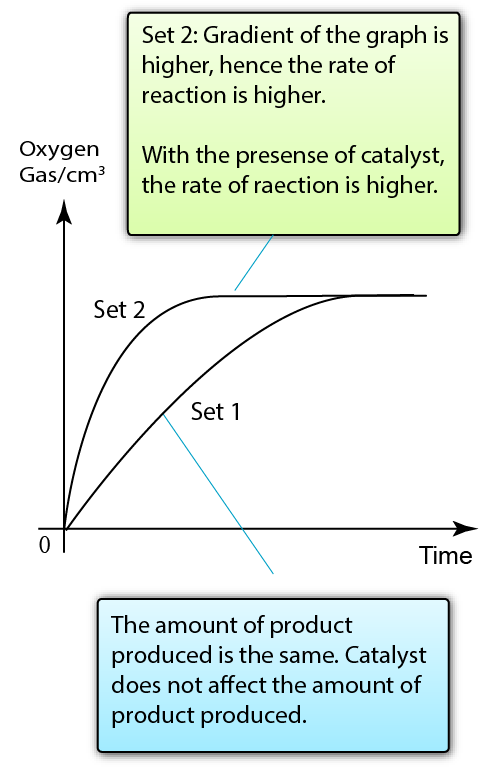
Set 1: Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
Set 2: Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide + Manganese(IV) Oxide (Catalyst)
Chemical Reaction:
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
Result:
Manganese(IV) oxide acts as a catalyst to increase the rate of reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid
Conclusion:
The presence of catalyst increases the rate of reaction
Note:
In SPM, you need to remember the catalyst used in both the chemical reaction above.
Characteristic of Catalyst
- A catalyst is a substance which can change the rate of reaction.
- There are a few things you need to know about catalyst:
- Chemically, the catalyst remains unchanged during a reaction.
- Catalyst does not change the quantity of the product.
- Catalyst is specific, which means different chemical reaction may have different catalyst.
- Just a small amount needed to achieve a big increase in the rate of reaction.
- More amount of catalyst used can further increase the rate of reaction.
- Catalyst in powder form can further increase the rate of reaction.
- Catalyst may undergo physical change in a reaction.