Question 1:
Oils and fats are the products of reactions between fatty acids and glycerol.
Figure 1 shows the structure of fatty acid P.
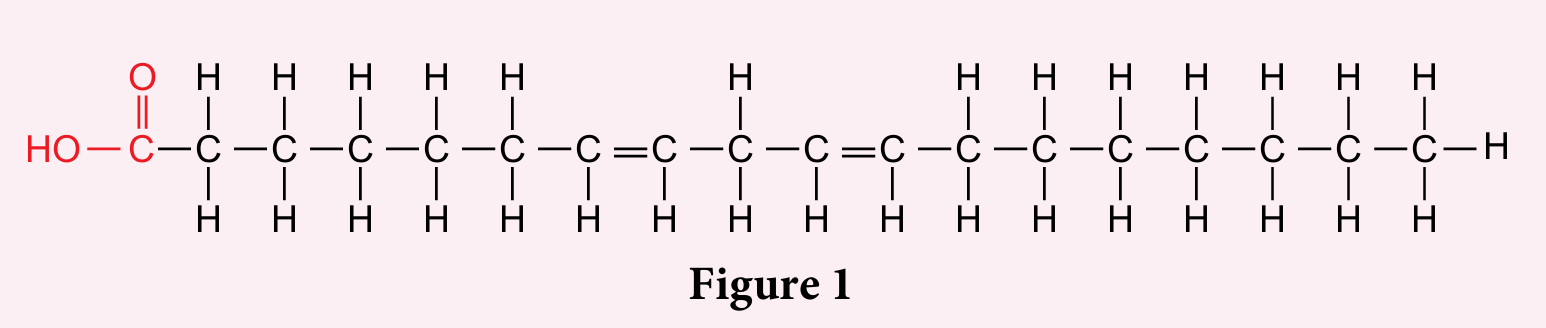
(a) State the type of fat produced when fatty acid P reacts with glycerol.
(b) Oils or fats that consist of fatty acid P easily oxidise and turn rancid when exposed to the air. Explain why.
Answer:
(a) Unsaturated fats
(b) The double covalent bonds in fatty acids P easily react with oxygen in the air and is further oxidised.
Oils and fats are the products of reactions between fatty acids and glycerol.
Figure 1 shows the structure of fatty acid P.

(a) State the type of fat produced when fatty acid P reacts with glycerol.
(b) Oils or fats that consist of fatty acid P easily oxidise and turn rancid when exposed to the air. Explain why.
Answer:
(a) Unsaturated fats
(b) The double covalent bonds in fatty acids P easily react with oxygen in the air and is further oxidised.
Question 2:
(a) The equation below shows the reaction for the preparation of soap in a laboratory.
Palm oil + concentrated sodium hydroxide → sodium palmitate (soap) + glycerol
(i) What is the name of the reaction?
(ii) What is the homologous series for palm oil?
(b) A pupil wants to prepare potassium palmitate soap.
What alkali should the pupil use?
Answer:
(a)(i) Saponification
(a)(ii) Ester
(b) Potassium hydroxide
(a) The equation below shows the reaction for the preparation of soap in a laboratory.
Palm oil + concentrated sodium hydroxide → sodium palmitate (soap) + glycerol
(i) What is the name of the reaction?
(ii) What is the homologous series for palm oil?
(b) A pupil wants to prepare potassium palmitate soap.
What alkali should the pupil use?
Answer:
(a)(i) Saponification
(a)(ii) Ester
(b) Potassium hydroxide
Question 3:
Figure 2 shows the cleansing results for clothes with greasy stains by using two different cleaning agents, A and B.
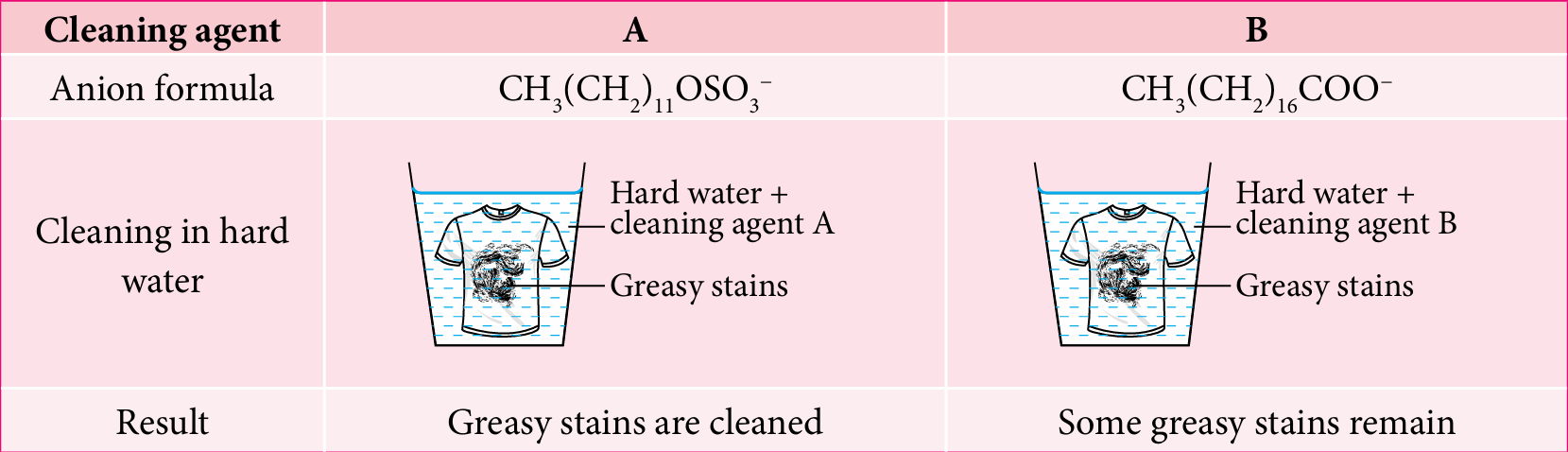
(a) State types of cleaning agents A and B.
(b) Based on Figure 2, compare and contrast the cleansing actions for both cleaning agents in hard water. Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
Cleansing agent A: Detergent
Cleansing agent B: Soap
(b)
Cleansing action of cleansing agent A is more effective in hard water, while cleaning agent B is less effective in hard water.
Hard water contains Ca2+ ions and Mg2+ ions.
Anions in cleansing agent B combine with these ions and form scum that is insoluble salts.
Cleansing agent A do not form scum.
Figure 2 shows the cleansing results for clothes with greasy stains by using two different cleaning agents, A and B.

(a) State types of cleaning agents A and B.
(b) Based on Figure 2, compare and contrast the cleansing actions for both cleaning agents in hard water. Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
Cleansing agent A: Detergent
Cleansing agent B: Soap
(b)
Cleansing action of cleansing agent A is more effective in hard water, while cleaning agent B is less effective in hard water.
Hard water contains Ca2+ ions and Mg2+ ions.
Anions in cleansing agent B combine with these ions and form scum that is insoluble salts.
Cleansing agent A do not form scum.
