Question 1:
The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that the particles in matter are constantly moving.
Mark (√) for true statements and (X) for false statements.
(a) At constant temperature, all particles move with the same velocity. ( )
(b) Particles in solids are moving freely. ( )
(c) Collisions between particles are random. ( )
(d) The kinetic energy of particles increases with increasing temperature. ( )
Answer:
(a) X
(b) X
(c) √
(d) √
The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that the particles in matter are constantly moving.
Mark (√) for true statements and (X) for false statements.
(a) At constant temperature, all particles move with the same velocity. ( )
(b) Particles in solids are moving freely. ( )
(c) Collisions between particles are random. ( )
(d) The kinetic energy of particles increases with increasing temperature. ( )
Answer:
(a) X
(b) X
(c) √
(d) √
Question 2:
Scientists use the collision theory to explain how chemical reactions occur. State two important conditions for effective collisions.
Answer:
Effective collision
• Has minimum energy to overcome the activation energy.
• Collide at the correct orientation to break and form chemical bonds.
Scientists use the collision theory to explain how chemical reactions occur. State two important conditions for effective collisions.
Answer:
Effective collision
• Has minimum energy to overcome the activation energy.
• Collide at the correct orientation to break and form chemical bonds.
Question 3:
Catalysts can help to speed up chemical reactions. How does a catalyst speed up a chemical reaction?
Answer:
• Catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway.
• Alternative reaction pathway has lower activation energy.
• More reactant particles can overcome the low activation energy.
• The frequency of effective collisions between the particles increases, hence the rate of reaction increases.
Catalysts can help to speed up chemical reactions. How does a catalyst speed up a chemical reaction?
Answer:
• Catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway.
• Alternative reaction pathway has lower activation energy.
• More reactant particles can overcome the low activation energy.
• The frequency of effective collisions between the particles increases, hence the rate of reaction increases.
Question 4:
All reactions including exothermic reactions and endothermic reactions have activation energy that must be overcome by reactant particles.
(a) What do you understand by the term activation energy?
(b) Mark and label the activation energy in Figure 7.28.
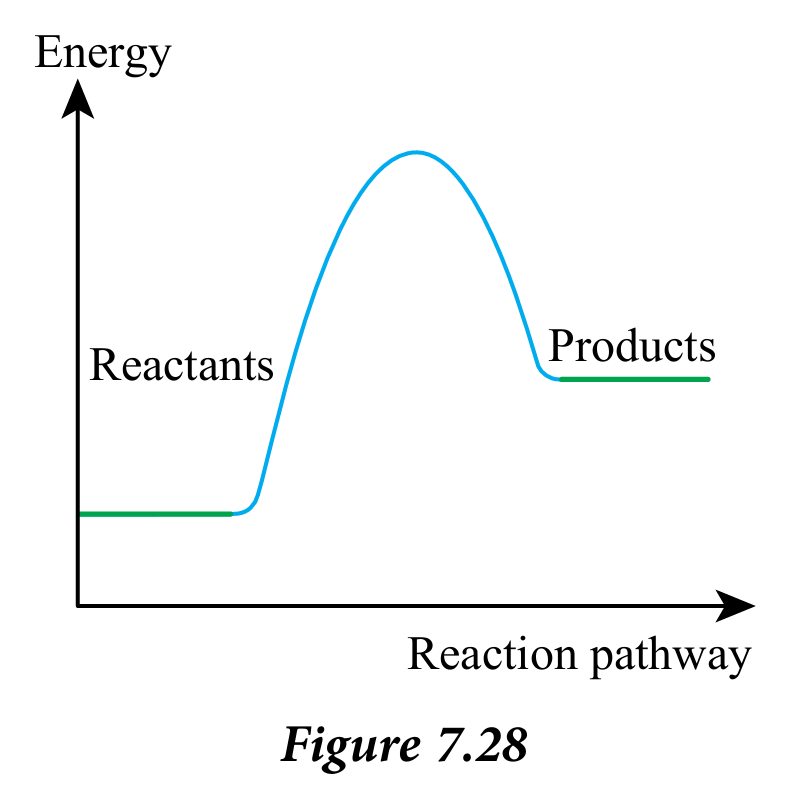
(c) Complete the following statements:
(i) Exothermic reactions heat to __________.
(ii) Endothermic reactions _________ heat from ___________.
Answer:
(a) Activation energy is the minimum energy that reactant particles must overcome in order for a reaction to occur.
(b)
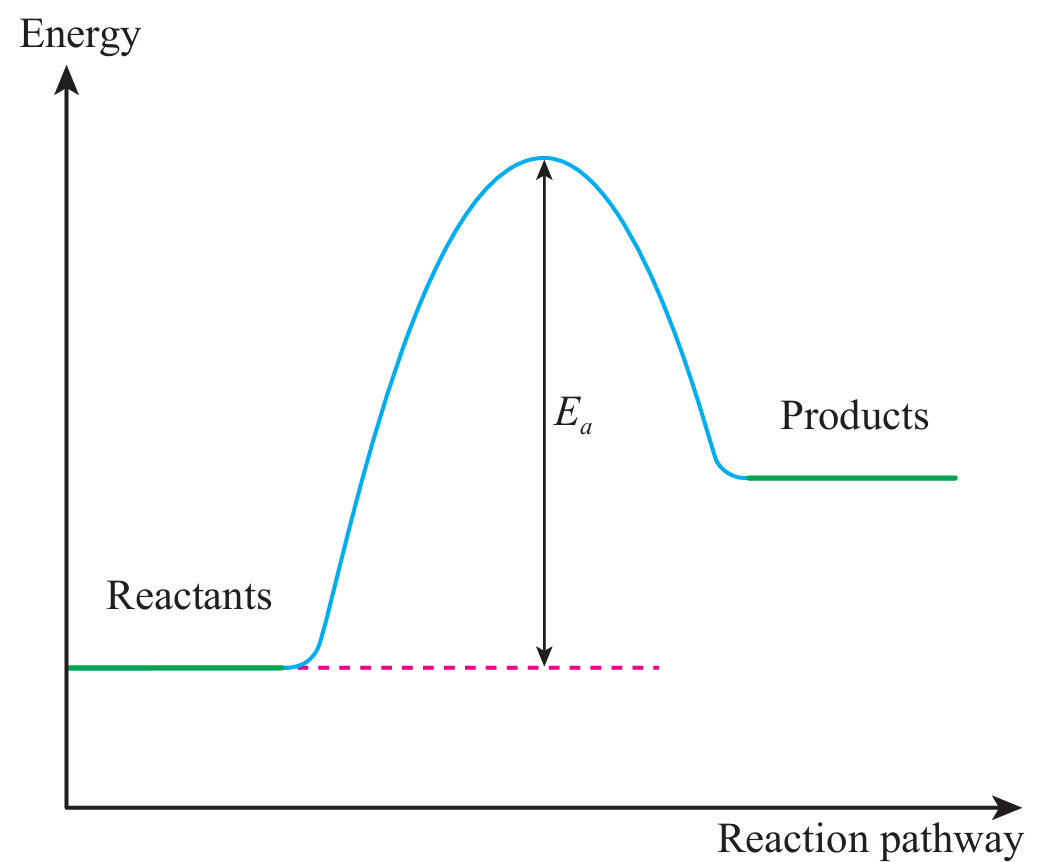
(c)(i) Exothermic reaction releases heat to the surroundings.
(c)(ii) Endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
All reactions including exothermic reactions and endothermic reactions have activation energy that must be overcome by reactant particles.
(a) What do you understand by the term activation energy?
(b) Mark and label the activation energy in Figure 7.28.

(c) Complete the following statements:
(i) Exothermic reactions heat to __________.
(ii) Endothermic reactions _________ heat from ___________.
Answer:
(a) Activation energy is the minimum energy that reactant particles must overcome in order for a reaction to occur.
(b)

(c)(i) Exothermic reaction releases heat to the surroundings.
(c)(ii) Endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
