Question 1:
Explain the meaning of rate of reaction.
Answer:
Rate of reaction is the change in the quantity of a reactant per unit time or the change in the quantity of product per unit time.
Explain the meaning of rate of reaction.
Answer:
Rate of reaction is the change in the quantity of a reactant per unit time or the change in the quantity of product per unit time.
Question 2:
Classify the following reactions as fast or slow:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Combustion of petrol in car engines
(c) Rusting of iron gate
(d) Explosion at oil factory
Answer:
(a) Slow
(b) Fast
(c) Slow
(d) Fast
Classify the following reactions as fast or slow:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Combustion of petrol in car engines
(c) Rusting of iron gate
(d) Explosion at oil factory
Answer:
(a) Slow
(b) Fast
(c) Slow
(d) Fast
Question 3:
State the observable and measurable change(s) to determine the rate of reaction in the following examples of reactions:
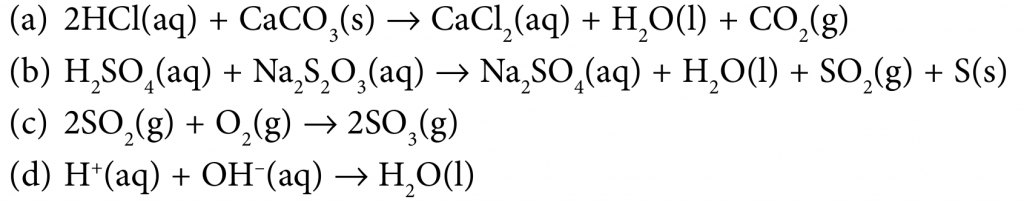
Answer:
(a) The increase in the volume of carbon dioxide gas, CO2 produced or the reduction in the mass of calcium carbonate, CaCO3.
(b) Formation of sulphur precipitate, S.
(c) Reduction in gas pressure.
(d) Reduction in the electrical conductivity or change in pH value of the neutralization reaction
State the observable and measurable change(s) to determine the rate of reaction in the following examples of reactions:
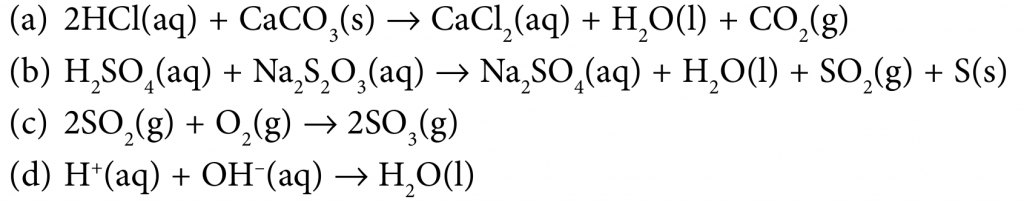
Answer:
(a) The increase in the volume of carbon dioxide gas, CO2 produced or the reduction in the mass of calcium carbonate, CaCO3.
(b) Formation of sulphur precipitate, S.
(c) Reduction in gas pressure.
(d) Reduction in the electrical conductivity or change in pH value of the neutralization reaction
Question 4:
Metals react with acids at different rates.

Three different metals, P, Q and R react separately with 100 cm3 of acid. The time taken to collect 50 cm3 of hydrogen gas for each of the metal is recorded in Table 7.4
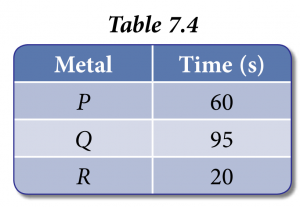
(a) Calculate the average rates of reaction for each of the metal with acid.
(b) Based on your answer in 4(a), arrange the three metals in order of descending reactivity.
Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} & P: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{60 \mathrm{~s}}=0.83 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \\ & Q: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{95 \mathrm{~s}}=0.53 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \\ & R: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{20 \mathrm{~s}}=2.50 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
R, P, Q. The higher the rate of reaction, the more reactive the metal.
Metals react with acids at different rates.
Three different metals, P, Q and R react separately with 100 cm3 of acid. The time taken to collect 50 cm3 of hydrogen gas for each of the metal is recorded in Table 7.4

(a) Calculate the average rates of reaction for each of the metal with acid.
(b) Based on your answer in 4(a), arrange the three metals in order of descending reactivity.
Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} & P: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{60 \mathrm{~s}}=0.83 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \\ & Q: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{95 \mathrm{~s}}=0.53 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \\ & R: \frac{50 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{20 \mathrm{~s}}=2.50 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
R, P, Q. The higher the rate of reaction, the more reactive the metal.
