Question 3:
A protein-digesting enzyme is used to study the effect of temperature on the rate of protein digestion in milk. The set-up of the apparatus is shown in Figure 1. The time measured is the time taken for the enzyme to digest all the protein and the milk becomes clear, that is until the ‘X’ mark is visible. Table 1 shows the results of the experiment.
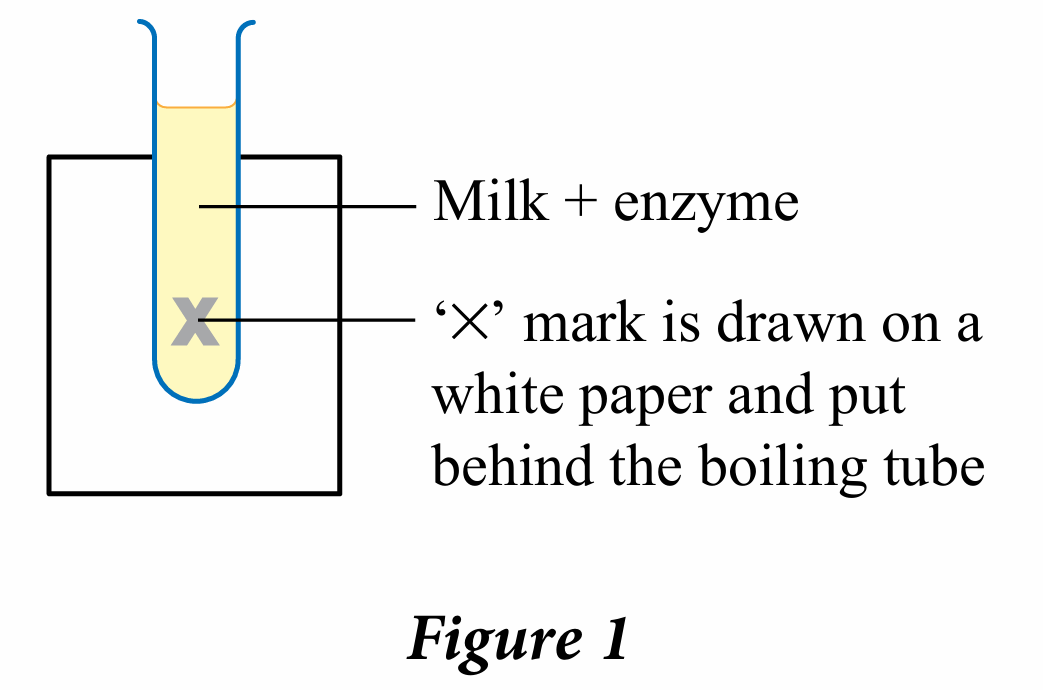
(a) State the changes that are observed and measured.
(b) State the manipulated variable and the fixed variables.
(c) The time of reaction is determined by measuring the time taken for the milk solution to turn clear.
(i) What is the relationship between the rate of reaction and time?
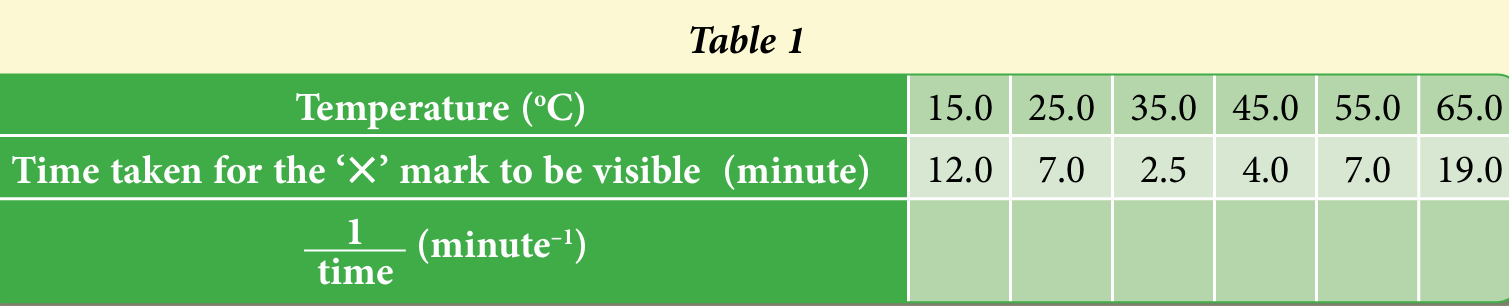
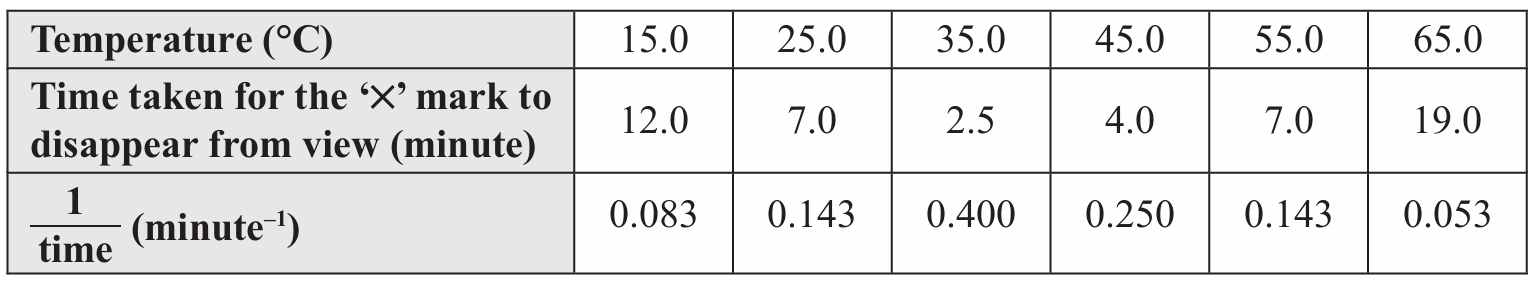
(ii) Complete Table 1 by calculating the value of 1/time .
(iii) Plot a graph of 1/time against temperature.
(iv) What conclusion can be formulated based on the graph in (c)(iii)?
Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a) Change in the murkiness of milk. The time taken for the ‘X’ mark to disappear from view.
(b)
Manipulated variable : Temperature
Fixed variable : Type of catalyst, volume and concentration of milk, size of boiling tubes, paper marked ‘X’
(c)(i) Rate of reaction is inversely proportional with time, that is rate = 1/time
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii)
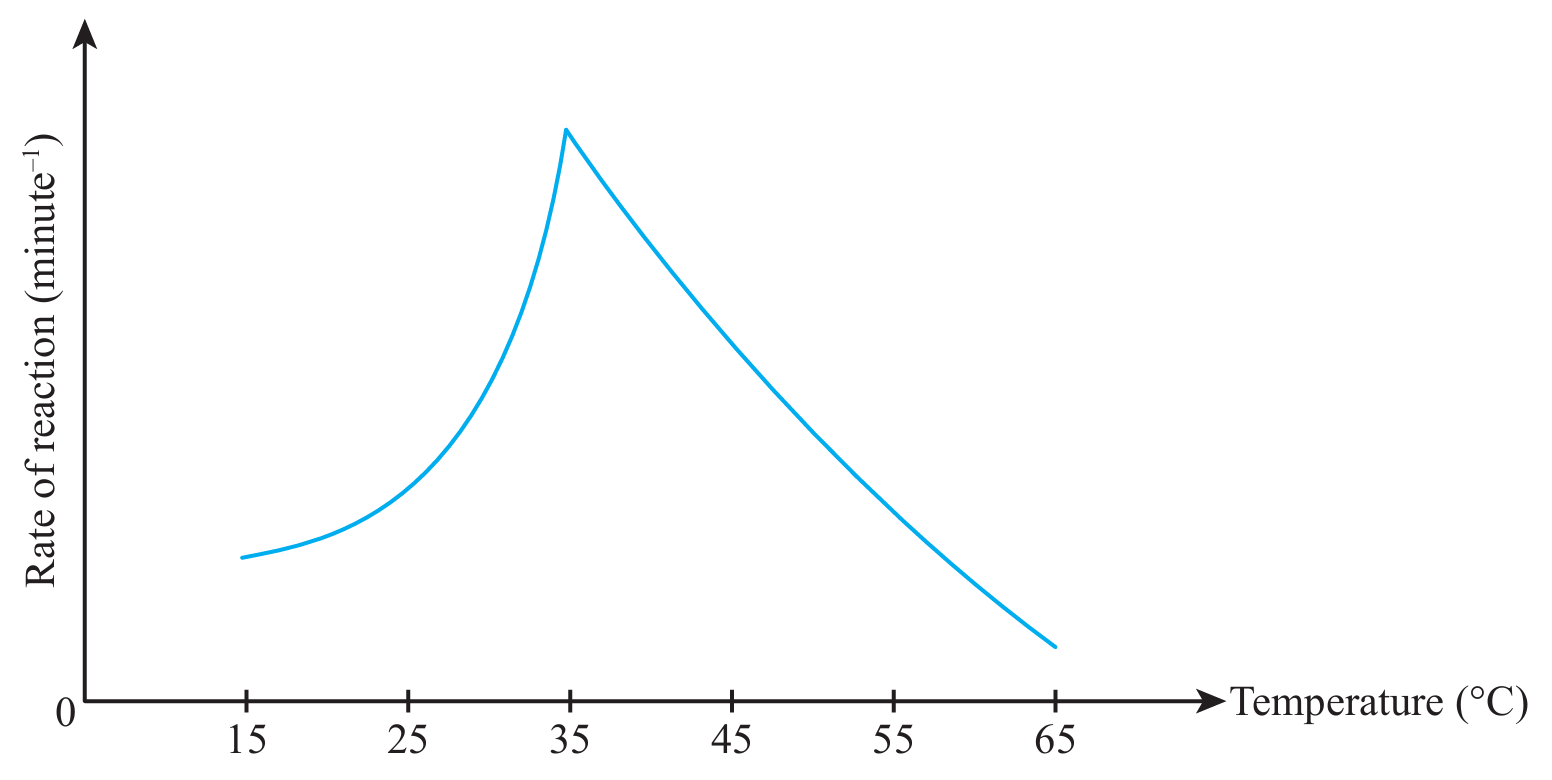
(c)(iv)
Rate of reaction increases and then decreases with the increase in temperature.
Initially, the rate of reaction increases because
(i) presence of catalyst increases the rate of reaction
(ii) increase of temperature increases the rate of reaction
Finally, the rate of reaction decreases because
(i) enzymes function optimally at 37 °C (body temperature).
(ii) enzymes get denatured at high temperature and lose their ability to increase the rate of reaction
A protein-digesting enzyme is used to study the effect of temperature on the rate of protein digestion in milk. The set-up of the apparatus is shown in Figure 1. The time measured is the time taken for the enzyme to digest all the protein and the milk becomes clear, that is until the ‘X’ mark is visible. Table 1 shows the results of the experiment.


(a) State the changes that are observed and measured.
(b) State the manipulated variable and the fixed variables.
(c) The time of reaction is determined by measuring the time taken for the milk solution to turn clear.
(i) What is the relationship between the rate of reaction and time?
(ii) Complete Table 1 by calculating the value of 1/time .
(iii) Plot a graph of 1/time against temperature.
(iv) What conclusion can be formulated based on the graph in (c)(iii)?
Explain your answer.
Answer:
(a) Change in the murkiness of milk. The time taken for the ‘X’ mark to disappear from view.
(b)
Manipulated variable : Temperature
Fixed variable : Type of catalyst, volume and concentration of milk, size of boiling tubes, paper marked ‘X’
(c)(i) Rate of reaction is inversely proportional with time, that is rate = 1/time
(c)(ii)

(c)(iii)

(c)(iv)
Rate of reaction increases and then decreases with the increase in temperature.
Initially, the rate of reaction increases because
(i) presence of catalyst increases the rate of reaction
(ii) increase of temperature increases the rate of reaction
Finally, the rate of reaction decreases because
(i) enzymes function optimally at 37 °C (body temperature).
(ii) enzymes get denatured at high temperature and lose their ability to increase the rate of reaction
Question 4:
The collision theory explains how reactant particles interact for reaction to occur and products formed.
(a) What are the two main principles of the collision theory?
(b) Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O, known as laughing gas, is produced from the following reaction:
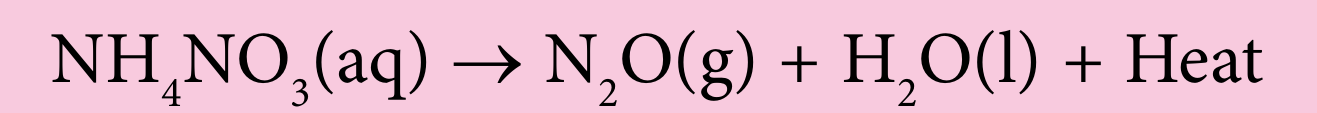
(i) Balance the above equation.
(ii) Draw the fully labelled energy profile diagram, including the activation energy, for the reaction.
(c) Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O reacts with nitrogen monoxide, NO to produce nitrogen, N2 and nitrogen dioxide, NO2.
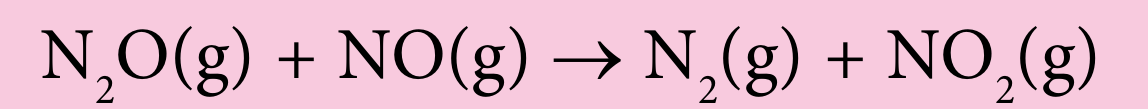
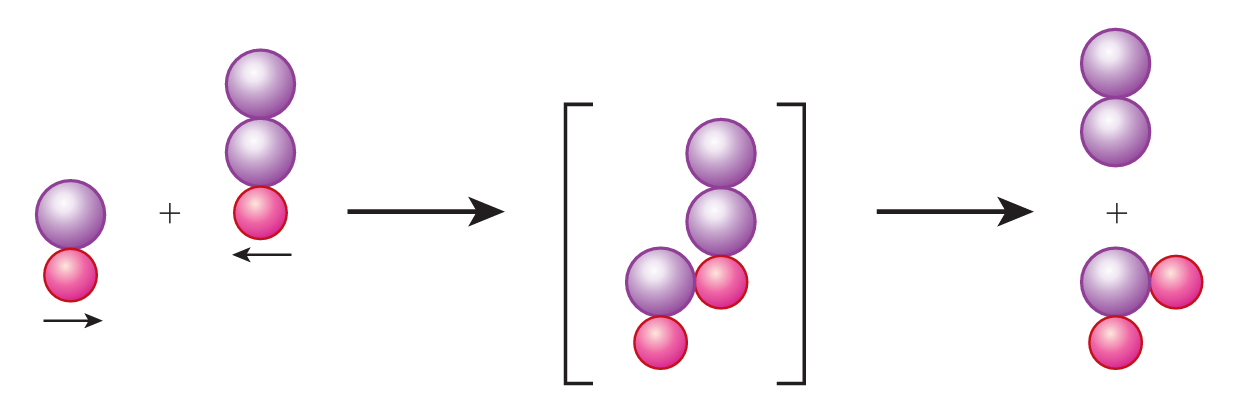
The reactants, dinitrogen monoxide, N2O and nitrogen monoxide, NO have to collide in the correct orientation to produce effective collisions and for the reaction to occur. Figure 2 shows the atomic arrangement of the reactants and products.
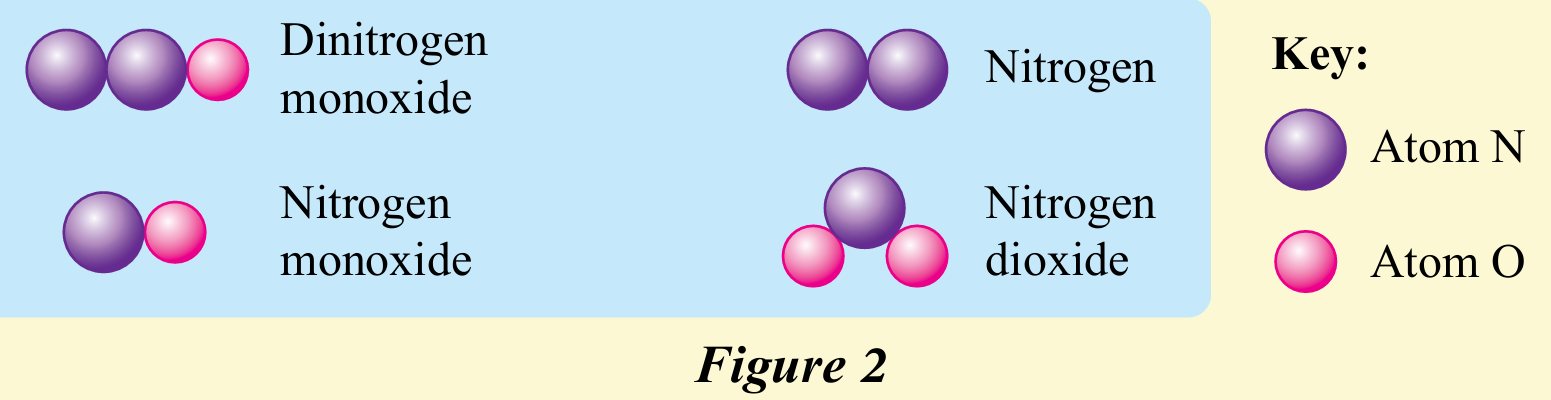
Draw the orientation of the reactant particles, dinitrogen monoxide, N2O and nitrogen monoxide, NO that results in effective collisions.
Answer:
(a)
Reactant particles must collide for a reaction to occur.
Rate of reaction depends on the frequency of effective collision.
(b)(i)
$$ \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{NO}_3(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{~g})+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})+\text { heat } $$
(b)(ii)
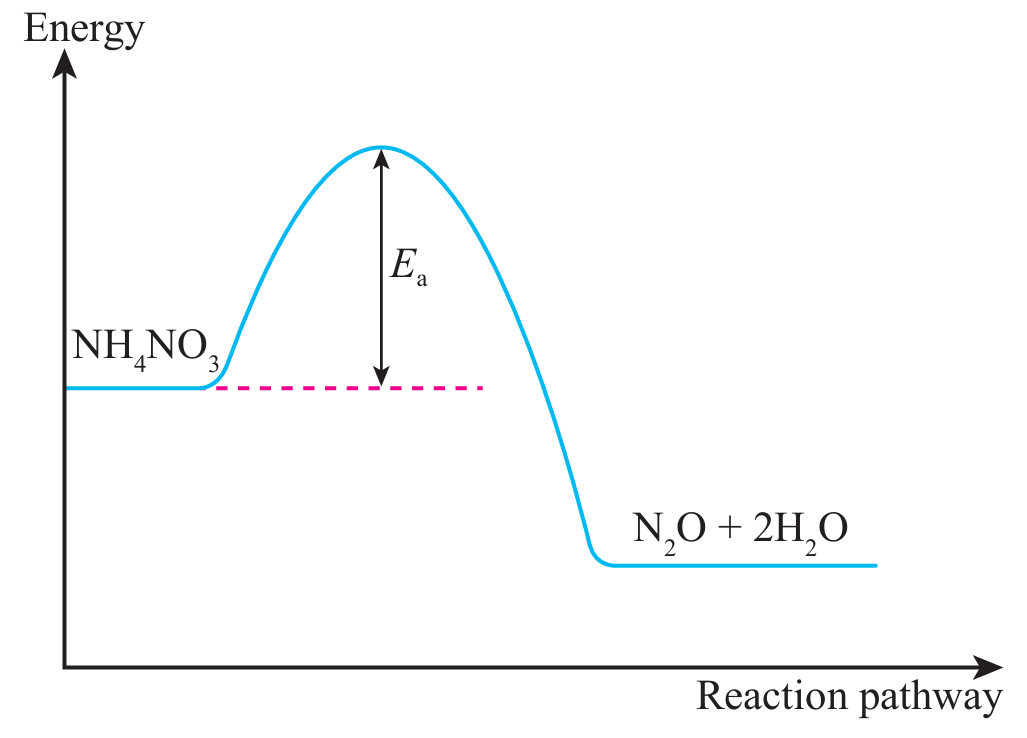
(c)
The collision theory explains how reactant particles interact for reaction to occur and products formed.
(a) What are the two main principles of the collision theory?
(b) Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O, known as laughing gas, is produced from the following reaction:
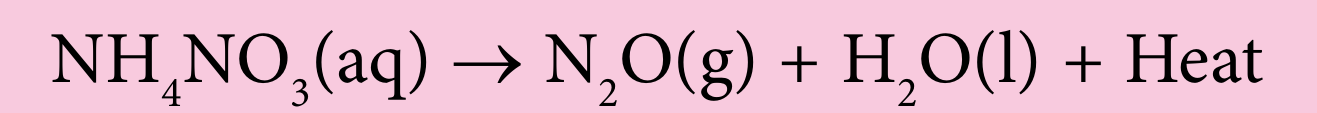
(i) Balance the above equation.
(ii) Draw the fully labelled energy profile diagram, including the activation energy, for the reaction.
(c) Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O reacts with nitrogen monoxide, NO to produce nitrogen, N2 and nitrogen dioxide, NO2.
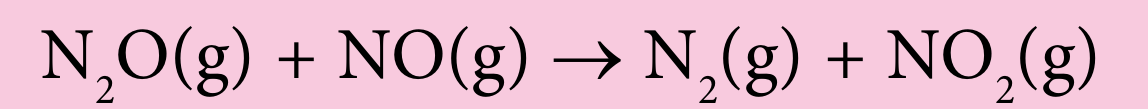
The reactants, dinitrogen monoxide, N2O and nitrogen monoxide, NO have to collide in the correct orientation to produce effective collisions and for the reaction to occur. Figure 2 shows the atomic arrangement of the reactants and products.

Draw the orientation of the reactant particles, dinitrogen monoxide, N2O and nitrogen monoxide, NO that results in effective collisions.
Answer:
(a)
Reactant particles must collide for a reaction to occur.
Rate of reaction depends on the frequency of effective collision.
(b)(i)
$$ \mathrm{NH}_4 \mathrm{NO}_3(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{~g})+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})+\text { heat } $$
(b)(ii)

(c)

