Analgesic
- An analgesic (colloquially known as painkiller) is any member of the diverse group of drugs used to relieve pain.
- Examples of frequently used analgesic are aspirin, paracetamol and codeine.
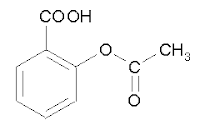
Aspirin
- Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is a drug in the family of salicylates, often used as an
- analgesic (against minor pains and aches),
- antipyretic (against fever), and
- anti-inflammatory (Such as arthritis).
- It has also an anticoagulant (blood thinning) effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent heart attacks.
Side Effect
- Several hundred fatal overdoses of aspirin occur annually, but the vast majority of its use is beneficial.
- Its primary undesirable side effects, especially in stronger doses, are gastrointestinal distress (including ulcers and stomach bleeding) and tinnitus.
- Another side effect, due to its anticoagulant properties, is increased bleeding in menstruating women.
Paracetamol
- Paracetamol (or acetaminophen), is a popular analgesic and antipyretic (against fever) drug that is used for the relief of fever, headaches, and other minor aches and pains.
- It is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications and many prescription analgesics.
- It is remarkably safe in standard doses, but because of its wide availability, deliberate or accidental overdoses are not uncommon.
- Due to its low side effect, paracetamol is used to replace aspirin especially treatments involve children.
- Panadol is one the most popular brand of paracetamol in Malaysia.
Codeine
- Codeine, when use in high dose, is an analgesic which stronger than aspirin and paracetamol.
- Approved indications for codeine include:
- cough – though its efficacy has been disputed.
- diarrhea
- mild-to-moderate pain
- Continuous consumption of codeine will cause addiction.