Question 6:
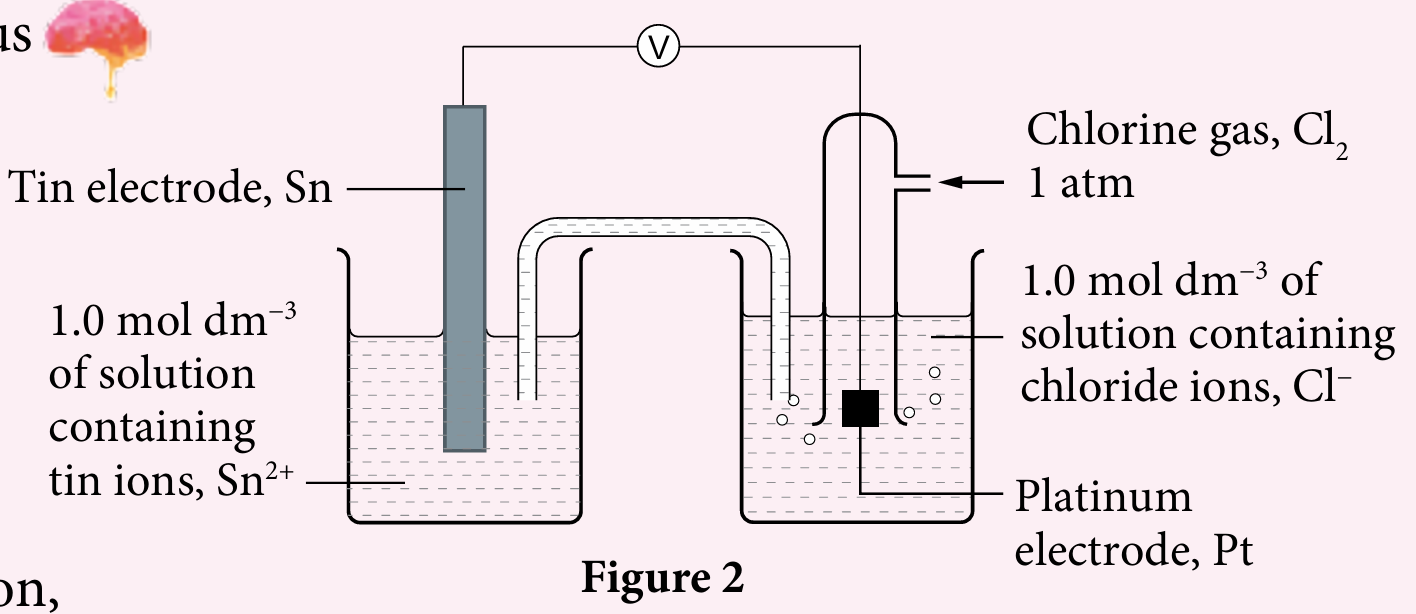
Figure 2 shows a set-up of apparatus for a voltaic cell. With reference to the half-cell standard electrode potential, E0:
(a) identify the negative and positive terminals.
(b) write the cell notation for the chemical cell.
(c) write the equations for reduction, oxidation and the overall ionic equation.
(d) calculate the voltage of the cell.
Answer:
(a) Negative terminal : Tin electrode.
Positive terminal : Platinum electrode.
(b) $$ \mathrm{Sn}(\mathrm{~s})\left|\mathrm{Sn}^{2+}\left(\mathrm{aq}, 1 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3}\right) \| \mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{aq}), \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\left(\mathrm{aq}, 1 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3}\right)\right| \mathrm{Pt}(\mathrm{~s}) $$
(c)
$$ \begin{array}{ll} \text { Oxidation reaction } & : \mathrm{Sn} \rightarrow \mathrm{Sn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \\ \text {Reduction reaction } & : \mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \\ \text {Ionic equation } & : \mathrm{Sn}^{-}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Sn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \end{array} $$
(d) $$ \mathrm{E}_{\text {cell }}^0=(+1.36)-(-0.14)=+1.50 \mathrm{~V} $$

Figure 2 shows a set-up of apparatus for a voltaic cell. With reference to the half-cell standard electrode potential, E0:
(a) identify the negative and positive terminals.
(b) write the cell notation for the chemical cell.
(c) write the equations for reduction, oxidation and the overall ionic equation.
(d) calculate the voltage of the cell.
Answer:
(a) Negative terminal : Tin electrode.
Positive terminal : Platinum electrode.
(b) $$ \mathrm{Sn}(\mathrm{~s})\left|\mathrm{Sn}^{2+}\left(\mathrm{aq}, 1 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3}\right) \| \mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{aq}), \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\left(\mathrm{aq}, 1 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3}\right)\right| \mathrm{Pt}(\mathrm{~s}) $$
(c)
$$ \begin{array}{ll} \text { Oxidation reaction } & : \mathrm{Sn} \rightarrow \mathrm{Sn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \\ \text {Reduction reaction } & : \mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \\ \text {Ionic equation } & : \mathrm{Sn}^{-}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Sn}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \end{array} $$
(d) $$ \mathrm{E}_{\text {cell }}^0=(+1.36)-(-0.14)=+1.50 \mathrm{~V} $$
Question 7:
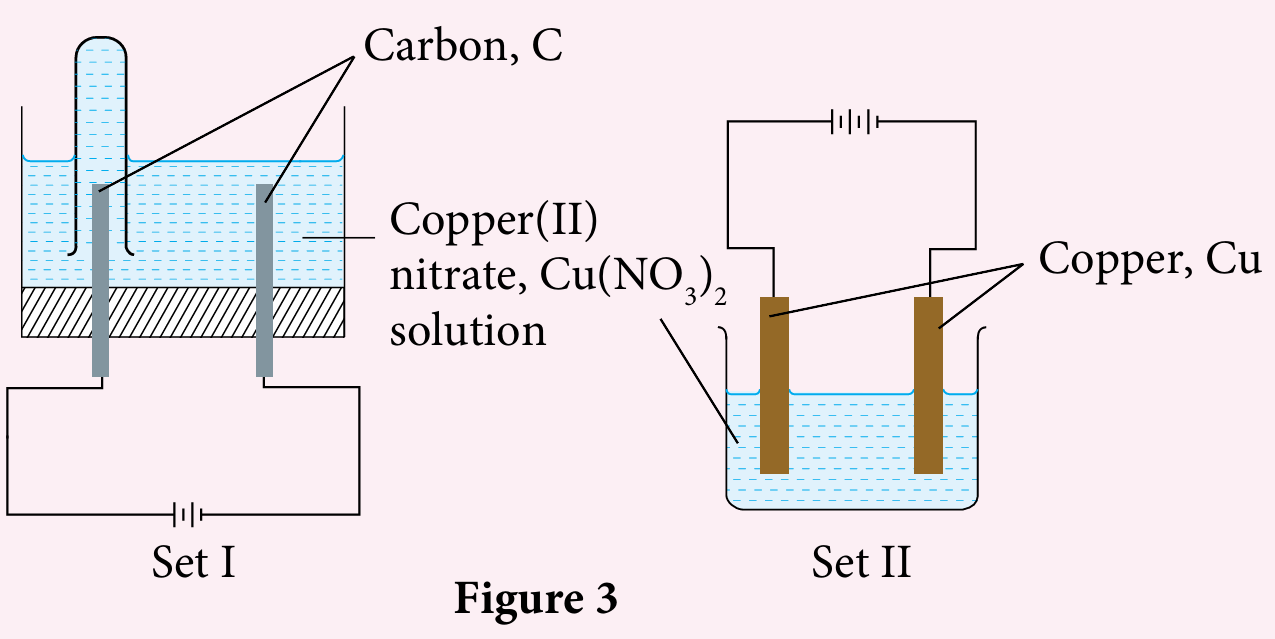
Figure 3 shows two sets of apparatus used to study the electrolysis of copper(II) nitrate solution.
(a) Name the product formed at the anode in set I.
Explain your answer.
(b) Describe, in brief, the chemical test to verify the product at the anode in set I.
(c) Compare the colour of copper(II) nitrate solution in Set I and Set II after the electrolysis is conducted for one hour. Explain your answers.
Answer:
(a) Oxygen gas. Hydroxide ion is discharged because the E0 value of OH− ion is less positive compared to the E0 value of NO3− ion.
Four OH− ions lose four electrons to form one oxygen molecule and two water molecules.
(b) Insert a glowing wooden splinter into the test tube. The glowing splinter rekindles.
(c) – The blue colour of copper(II) sulphate solution becomes paler in Set I, but the blue colour of copper(II) sulphate solution remains unchanged in Set II.
– The concentration of Cu2+ ions decreases in Set I, but the concentration of Cu2+ ions remains unchanged in Set II.
– Cu2+ ions are discharged to form copper atoms at the cathode in Set I, but in Set II, the discharge rate of Cu2+ ions to form copper atoms at the cathode is the same as the ionisation rate of copper atoms to form Cu2+ ions at the anode.

Figure 3 shows two sets of apparatus used to study the electrolysis of copper(II) nitrate solution.
(a) Name the product formed at the anode in set I.
Explain your answer.
(b) Describe, in brief, the chemical test to verify the product at the anode in set I.
(c) Compare the colour of copper(II) nitrate solution in Set I and Set II after the electrolysis is conducted for one hour. Explain your answers.
Answer:
(a) Oxygen gas. Hydroxide ion is discharged because the E0 value of OH− ion is less positive compared to the E0 value of NO3− ion.
Four OH− ions lose four electrons to form one oxygen molecule and two water molecules.
(b) Insert a glowing wooden splinter into the test tube. The glowing splinter rekindles.
(c) – The blue colour of copper(II) sulphate solution becomes paler in Set I, but the blue colour of copper(II) sulphate solution remains unchanged in Set II.
– The concentration of Cu2+ ions decreases in Set I, but the concentration of Cu2+ ions remains unchanged in Set II.
– Cu2+ ions are discharged to form copper atoms at the cathode in Set I, but in Set II, the discharge rate of Cu2+ ions to form copper atoms at the cathode is the same as the ionisation rate of copper atoms to form Cu2+ ions at the anode.
