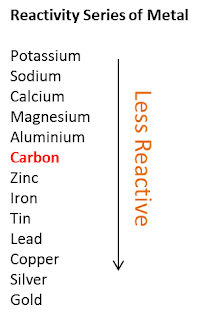
Position of Carbon in The Series of Reactivity of Metals
- The position of carbon in the series of reactivity of metals can be determined based on:
- the ability of metals to take away oxygen from carbon oxide, that is carbon dioxide.
- the ability of carbon to take away oxygen from metal oxides
Experiment 1
- If the metal can take away oxygen from carbon dioxide, then the metal is more reactive than carbon.Metal + carbon dioxide → metal oxide + carbon
- On the other hand, if the metal cannot take away oxygen from carbon dioxide, then the metal is less reactive than carbon.
Example
2Mg (s) + CO2(g) → 2MgO (s) + C (s)
Conclusion: Magnesium is more reactive than carbon.
Experiment 2
- If carbon can take away oxygen from metal oxide, then the carbon is more reactive than the metal.Carbon + metal oxide → metal + carbon dioxide
- On the other hand, if carbon cannot take away oxygen from metal oxide, then the carbon is less reactive than the metal.
Example
C + 2CuO → 2Cu + CO2
Conclusion: Copper is less reactive than carbon.