History of Development of the Model of Atom
Table below shows the scientists that contribute to the development of the Model of Atom.
John Dalton
|
|
J.J. Thomson 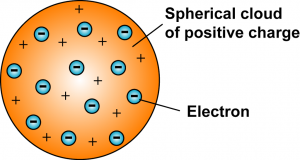 |
The electrons were positioned uniformly throughout the atom. |
Ernest Rutherford
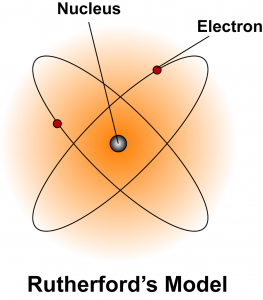 |
|
Neils Bohr
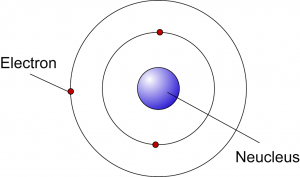 |
|
James Chadwick
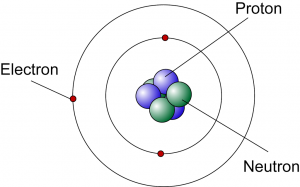 |
|
Recommended Videos
Models of the Atom Timeline
Models of the Atom: Thompson, Rutherford and Bohr Models
Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model of the Atom
Modern Atomic Model
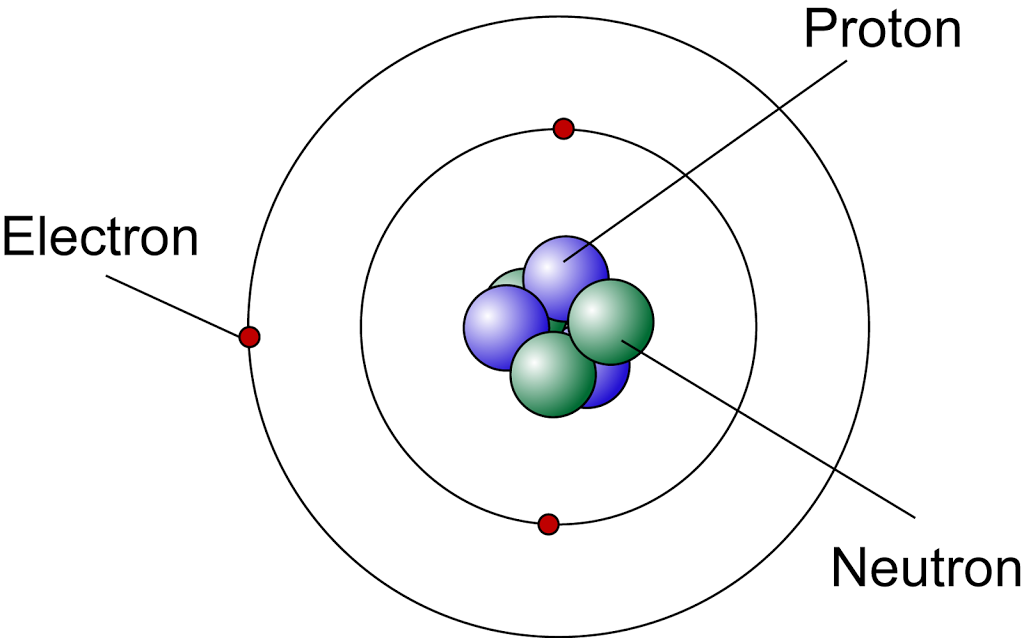
According to the modern atomic model,
- The central nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. It containing almost all the mass of the atom.
- the nucleus of an atom is very small compared to the size of the atom
- the electrons are orbiting outside the nucleus in the electron shells
- the electrons are moving in electron shells at a very high speed and we cannot determine the position of the electrons at a particular time
The Subatomic Particles of an Atom
- Atoms are made up of tiny particles called subatomic particles.
- An atom contains three types of subatomic particles:
- proton,
- neutron and
- electron,
- The proton and neutron form the nucleus at the centre of an atom. They are also called the nucleon of an atom.
- The electron moves around the nucleus at a very high speed.
- The nucleus is positively charged because of the presence of protons, which are positively charged. The neutrons are neutral.
- The symbols, charge and relative masses of proton, neutron and electron are as below.
| Particle | Symbol | Relative charge | Relative mass |
| Proton |
p |
+1 |
1 |
| Neutron |
n |
0 |
1 |
| Electron |
e |
-1 |
1/1840 |
The Charge of Particles
- A neutral atom contains the same number of electrons as the protons.
- The positive and negative charges of the protons and electrons respectively neutralise each other, for example, (+4) + (-4) = 0
- If the number of protons is greater than the number of electron, the particle is positively charge.
- If the number of protons is greater than the number of electron, the particle is positively charge.
| Number of proton | Number of electron |
Charge |
|
3 |
3 |
0 |
|
5 |
2 |
+3 |
|
9 |
10 |
-1 |
|
11 |
10 |
+3 |
|
16 |
18 |
-2 |
|
17 |
18 |
-1 |
|
20 |
18 |
+3 |
Proton Number and Nucleon Number
- Proton number = the number of protons
- Nucleon number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
Proton Number
- The proton number (Z) represent the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom.
- Proton number = the number of protons
- The proton number is also known as the atomic number.
- In an atom of neutral charge, the number of electrons also equals the atomic number.
- Hence, the proton number of an atom can also represent the number of electrons.
Nucleon Number
- The nucleon number (A), also called atomic mass number or mass number, is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atomic nucleus. (Nucleon number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons)
- The nucleon number of an atom is about the same as the mass of the atom because the mass of an electron is very small and can be ignored.
|
Atom |
Proton Number |
Nucleon Number |
Amount of Proton |
Amount of electron |
Amount of Neutron |
| Helium |
2 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| Oxygen |
8 |
16 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
| Sodium |
11 |
23 |
11 |
11 |
12 |
| Chlorine |
17 |
35 |
17 |
17 |
18 |
[Notes: In ion, the amount of protons IS NOT equal to the amount of electrons]
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of certain elements which have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atoms.
It can also be defined as atoms of certain elements with the same proton numbers but with different nucleon numbers.
Properties of Isotope
|
|
| Number of proton | equal |
| Number of neutron | difference |
| Chemical properties | same |
| Physical properties | difference |
Example:
| Element | Name | Symbol | Proton Number | Nucleon Number | Number of proton | Number of neutron |
| Hydrogen | Hydrogen |
11H
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
| Deuterium |
21H
|
1
|
12
|
1
|
1
|
|
| Tritium |
31H
|
1
|
23
|
1
|
2
|
|
| Oxygen | Oxygen-16 |
168O
|
8
|
16
|
8
|
8
|
| Oxygen-17 |
178O
|
8
|
17
|
8
|
9
|
|
| Oxygen-18 |
188O
|
8
|
18
|
8
|
10
|
|
| Carbon | Carbon-12 |
126C
|
6
|
12
|
6
|
6
|
| Carbon-13 |
136C
|
6
|
13
|
6
|
7
|
|
| Carbon-14 |
146C
|
6
|
14
|
6
|
8
|
|
| Chlorine | Chlorine-35 |
3517Cl
|
17
|
35
|
17
|
18
|
| Chlorine-37 |
3717Cl
|
17
|
37
|
17
|
20
|
|
| Sodium | Sodium-23 |
2311Na
|
11
|
23
|
11
|
12
|
| Sodium-24 |
2411Na
|
11
|
24
|
11
|
13
|
Menu