Plastics
- Plastics are light, strong and do not react with any chemical substances, like acids and alkalis.
- They can be made into many shapes and sizes.
- They are also good insulators of heat and electricity.
Examples of Plastics:
Polythene (polyethylene)
Structure
Monomer: Ethene
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
Uses: Plastic bags containers and cups
Advantages: light and strong
Polyvinyl chloride or PVC (polychloroethene)
Structure
Monomer: Chloroethene
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
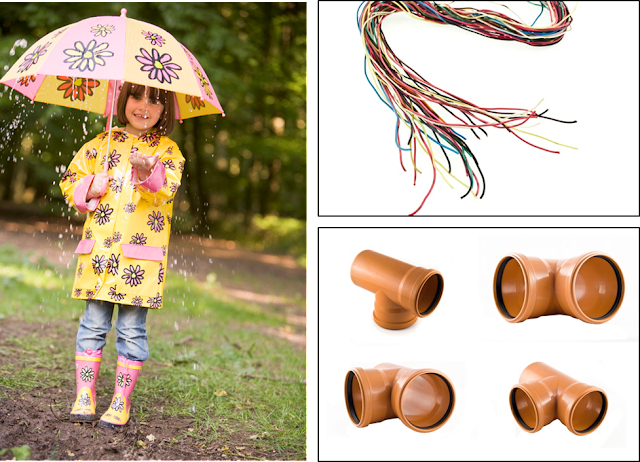
Uses: Raincoat, Pipes to insulate electric wires
Advantages: can be coloured; heat resistant
Polystyrene (polyphenylethene)
Structure
Monomer: Phenylethene
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
Uses: Packaging materials, children toys, ball-point pens, as heat and electric insulators
Advantages: light and strong
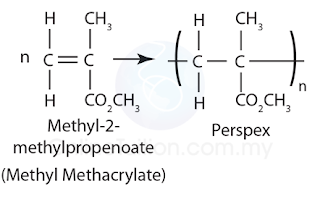
Perspex (polymethyl 2-methyl propenoate)
Structure
Monomer: Methyl-2-methylpropenoate
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
Uses: Aeroplane window panes, Lenses, car lamp covers
Advantages: light, strong, translucent, stable towards sunlight
Polypropene
Structure
Monomer: Propene
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
Uses: Plastics, Bottles, plastic tables and chairs
Advantages: strong and light
Teflon (polytetrafluoroethene or PTFE)
Structure
Monomer: Tetrafluoroethene
Produced by polymerisation: Addition
Uses: To make non-sticky pots and pans
Advantages: hard, can withstand high temperatures and corrosives chemicals