Ionic Compounds
Structure Ionic Compound
- In an ionic compound, the alternate positive and negative ions in an ionic solid are arranged in an orderly way as shown in the image to the right.
- The ions can form a giant ionic lattice structure with ionic bond between the ions.
- The ionic bond is the strong electrical attraction (electrostatic force) between the positive and negative ions next to each other in the lattice.
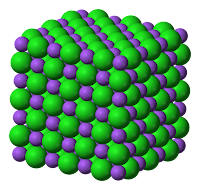 |
| (Giant Lattice Structure) |
 |
| (Strong Electrostatic Force formed between the positive and negative ions) |
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- The strong bonding force makes ionic compounds has high melting and boiling points.
- All ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature.
- They are hard but brittle, when stressed the bonds are broken along planes of ions which shear away.
- Many, ionic compounds (but not all) are soluble in water.
- The solid crystals DO NOT conduct electricity because the ions are not free to move to carry an electric current.
- However, if the ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the liquid will now conduct electricity, as the ion particles are now free.

