Structure Question 3:
The table below shows the melting and boiling points of three different substances.
Substance | Melting Point | Boiling Point |
H | -120°C | -5°C |
I | 45°C | 98°C |
J | 10°C | 350°C |
Answer:
- What is the physical state of H, I and J at room temperature (25°C)?
H: gaseous I: solid J: liquid - Which substance diffuses the fastest at room temperature? Explain your answer.
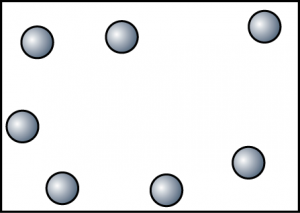
Substance H. Because substance H exist as a gas at room temperature, hence there is a lot of empty space between the particles. Other than that, the particles of H have the highest kinetic energy. - Draw some diagrams to show the arrangement of particles of substance I at 40°C, 80°C and 120°C.At 40°C
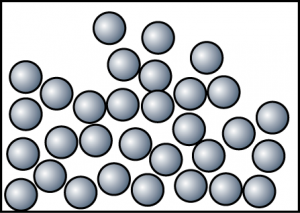
At 80°C
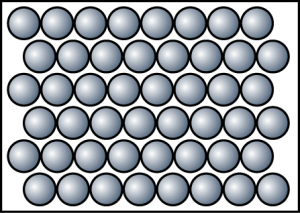
At 120°C
- What is the name of the process which atoms or molecules of a substance in liquid state gain sufficient energy to enter the gaseous state below boiling point?
Evaporation - Define boiling point.
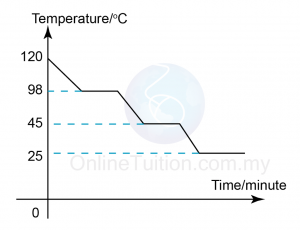
Boiling Point is the temperature at which the pressure exerted by the surroundings upon a liquid is equalled by the pressure exerted by the vapour of the liquid. - Sketch the graph of temperature against time for substance I when it is cooled from 120°C to room temperature.