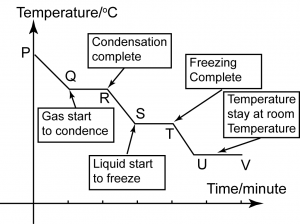
Cooling Curve
P
- The substance exists in gaseous state.
- The particles have very high energy and are moving randomly.
- The intermolecular forces between the particles are very weak and can be ignored.
P-Q
- The substance is in gaseous state.
- The particles lose kinetic energy during cooling, the particles getting closer to each other and the temperature drops.
Q
- The substance still exists as a gas.
- As the molecules are close enough, stronger forces of attraction result in forming of intermolecular bonds.
- The gas begins to condense and become liquid.
Q-R
- The process of condensation going on.
- Stronger bonds form as gas changes into liquid.
- The substance exists in both gaseous and liquid states.
- The temperature remains unchanged.
- This is because the energy produced during the formation of bonds is equal to the heat energy released to the surroundings during cooling.
- This constant temperature is the boiling point.
- The heat energy that releases during this condensation process is called the latent heat of vaporization.
R
- The substance exists only in liquid state as all the gas particles have condensed into liquid.
R-S
- The substance exists as a liquid.
- As the temperature falls, the naphthalene molecules lose heat energy. Their movement shows down and they move closer to each other.
S
- The substance still in liquid state.
- The particles have very little energy and begin to move closer towards one another as it starts to freeze into solid.
S-T
- The liquid is changing into solid form.
- Molecules rearrange to form the molecular arrangement of a solid.
- The substance exists as both liquid and solid.
- The temperature remains constant until all the liquid changes to solid.
- This is because the energy released is the same as the energy lost to the surroundings during cooling.
- This constant temperature is the freezing point.
- The heat energy that releases during this freezing process is called the latent heat of fusion.
T
- All the liquid freezes into solid. The particles are now closely packed in an orderly manner.
T-U
- Once all the liquid has become solid, the temperature falls once again until it reaches room temperature. The substance is in the solid state here.
U
- The substance reaches room temperature and remain at this temperature as long as the room temperature remain the same.