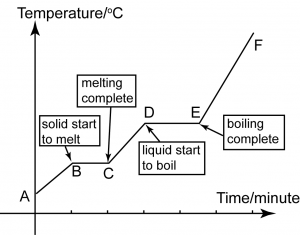
Heating Curve
A
- Naphthalene is in solid state at any temperature below its melting point.
- The particles are very closely packed together in an orderly manner.
- The forces between the particles are very strong. The particles can only vibrate at a fixed position.
A-B
- As the naphthalene is heated, heat energy is converted to kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy increases and the molecules vibrate faster about their fixed positions and the temperature increases.
B
- Naphthalene is still in solid state.
- Naphthalene molecules have received enough energy to overcome the forces of attraction between them.
- Some of the particles that gain enough energy begin to move freely.
- Naphthalene starts to melt and changes into a liquid.
B-C
- Naphthalene exists in both solid and liquid states.
- The temperature remains constant because the heat that supplied to naphthalene is used to overcome the forces of attraction that hold the particles together.
- The constant temperature is called the melting point.
- The heat energy that absorbed to overcome the intermolecular forces is named as the latent heat of fusion.
C
- All the naphthalene has completely melted.
- Solid naphthalene has turned into liquid.
C-D
- Naphthalene is in liquid state.
- As the liquid naphthalene is heated, the molecules gain more heat energy and the temperature continues to increase.
- The particles move faster and faster because their kinetic energy is increasing.
D
- Naphthalene still exists in liquid state.
- Naphthalene molecules have received enough energy to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles in the liquid.
- Some of the naphthalene molecules start to move freely and liquid naphthalene begin to change into gas.
D-E
- Naphthalene exists in both liquid and gaseous states.
- The temperature remains unchanged.
- The is because the heat energy absorbed is used to overcome the intermolecular forces between the particles of the liquid rather than increase the temperature of the liquid.
- This constant temperature is the boiling point.
E
- All the naphthalene has turn into gas.
E-F
- The gas particles continue to absorb more energy and move faster.
- The temperature increases as heating continues.