Question 1:
Polymerisation is a process of producing long chain molecules from monomers.
(a) Draw the monomers for polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
(b) What is the type of polymerisation involved in the production of PVC?
(c) The table below shows the information about polyethene and its monomer.

(i) State the use of polyethene.
(ii) Explain the difference between the physical state of ethene and polyethene.
Answer:
(a)
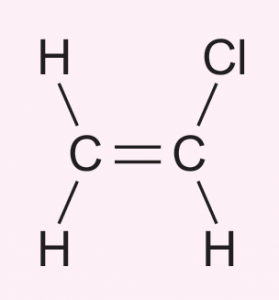
(b) Addition polymerisation.
(c) Production of plastic bottles.
(d) A polymer has a higher boiling point than its monomer due to the high intermolecular force of attraction between polymer chains.
Polymerisation is a process of producing long chain molecules from monomers.
(a) Draw the monomers for polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
(b) What is the type of polymerisation involved in the production of PVC?
(c) The table below shows the information about polyethene and its monomer.

(i) State the use of polyethene.
(ii) Explain the difference between the physical state of ethene and polyethene.
Answer:
(a)

(b) Addition polymerisation.
(c) Production of plastic bottles.
(d) A polymer has a higher boiling point than its monomer due to the high intermolecular force of attraction between polymer chains.
Question 2:
Polymers can be classified into natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
(a) Give an example of each type of polymer.
(b) Explain the difference between natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
(c) Melamine is a thermosetting synthetic polymer.
(i) What is the meaning of thermosetting polymer?
(ii) State the disadvantages of using thermosetting polymers.
Answer:
(a)
Natural polymer: polyisoprene.
Synthetic polymer: Polyvinyl chloride.
(b) Natural polymers can be found in nature, while synthetic polymers are man-made through a chemical reaction.
(c)(i) Thermosetting polymer is a polymer that cannot be remoulded after heating.
(c)(ii) Hard to decompose naturally and difficult to be disposed of.
Polymers can be classified into natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
(a) Give an example of each type of polymer.
(b) Explain the difference between natural polymers and synthetic polymers.
(c) Melamine is a thermosetting synthetic polymer.
(i) What is the meaning of thermosetting polymer?
(ii) State the disadvantages of using thermosetting polymers.
Answer:
(a)
Natural polymer: polyisoprene.
Synthetic polymer: Polyvinyl chloride.
(b) Natural polymers can be found in nature, while synthetic polymers are man-made through a chemical reaction.
(c)(i) Thermosetting polymer is a polymer that cannot be remoulded after heating.
(c)(ii) Hard to decompose naturally and difficult to be disposed of.
Question 3:
A student carried out an experiment to investigate the elasticity of natural rubber and vulcanised rubber by using the same sized rubber strips. Figure 1 shows the observation obtained from the experiment.
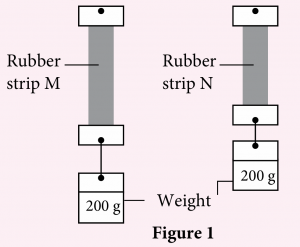
(a) Based on the observation, which strip is a natural rubber strip? Explain your answer.
(b) Which strip will snap first if the mass of the weight continues to increase?
Answer:
(a) Rubber strip M because natural rubber is softer, easily stretched and less elastic.
(b) Rubber strip M
A student carried out an experiment to investigate the elasticity of natural rubber and vulcanised rubber by using the same sized rubber strips. Figure 1 shows the observation obtained from the experiment.

(a) Based on the observation, which strip is a natural rubber strip? Explain your answer.
(b) Which strip will snap first if the mass of the weight continues to increase?
Answer:
(a) Rubber strip M because natural rubber is softer, easily stretched and less elastic.
(b) Rubber strip M
